Diffusion Chamber
⇰ Science Topic information page
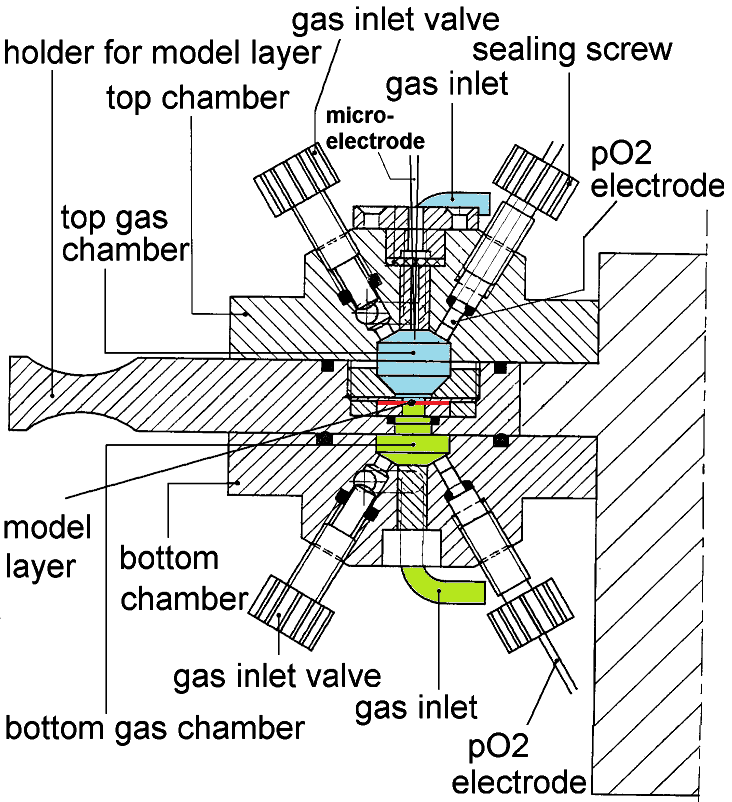 The diffusion chamber considered here is to measure gas fluxes through a flat
layer. At either side of the layer, a compartment can be closed or flushed with
a gas mixture. Measurements are by
oxygen electrodes
in each chamber. Later, a microelectrode was added to measure inside the layer.
Click the figure to see it in full detail.
The diffusion chamber considered here is to measure gas fluxes through a flat
layer. At either side of the layer, a compartment can be closed or flushed with
a gas mixture. Measurements are by
oxygen electrodes
in each chamber. Later, a microelectrode was added to measure inside the layer.
Click the figure to see it in full detail.
The standard procedure is, flushing both chambers until a steady profile in the
layer can be expected, then closing at least one chamber and recording the
oxygen partial pressure
PO2 in the chamber(s). From the in- or decrease, conclusions about
the fluxes into or out of the chambers can be drawn, but that is not as simple
as would be expected. The reason is, that there is a gas mixture, mostly,
nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2), and that both gases diffuse
at a different rate causing volume changes in the gas chambers. For an inert
flat layer, the oxygen pressure change in an adjacent closed chamber
is (1).
| dP |
= |
ART |
|
℘ |
(1 − c P)ΔP |
| dt |
V |
L |
where P is oxygen partial pressure, A exposed surface area of the layer, R gas
constant, T absolute temperature, ℘ oxygen permeability of the layer,
ΔP oxygen pressure difference across the layer, and c a correction term.
The correction term depends on stiffness of the layer and permeabilities of
the co-diffusing gases. For an inflexible layer, c would be zero. Else, for a
nitrogen-oxyen gas mixture:
| c = |
1 − ℘N2/℘O2 |
| (1 + η)PTot |
where η depends on layer stiffness and PTot is the total gas
pressure in the chamber.
So, for inert flat layer also a measurement of permeability ratio is possible.
This needs a correct analysis of both chamber recordings but results can be quite
accurate (1),(2).
(1) Hoofd L de Koning J Kreuzer F Lamboo A:
Determination of permeabilities for two gases from recording the partial pressure
of one gas. Pflügers Arch - Eur J Physiol 407(3): 320-326 (1986).
(2) Hoofd L Lamboo A: Oxygen permeability
of methemoglobin solutions soaked in Millipore filters. In: Oxygen Transport to
Tissue VII, Adv Exper Med Biol 191: 565 570 (1985).
Back to the top of the topic
–
 The diffusion chamber considered here is to measure gas fluxes through a flat
layer. At either side of the layer, a compartment can be closed or flushed with
a gas mixture. Measurements are by
oxygen electrodes
in each chamber. Later, a microelectrode was added to measure inside the layer.
Click the figure to see it in full detail.
The diffusion chamber considered here is to measure gas fluxes through a flat
layer. At either side of the layer, a compartment can be closed or flushed with
a gas mixture. Measurements are by
oxygen electrodes
in each chamber. Later, a microelectrode was added to measure inside the layer.
Click the figure to see it in full detail.